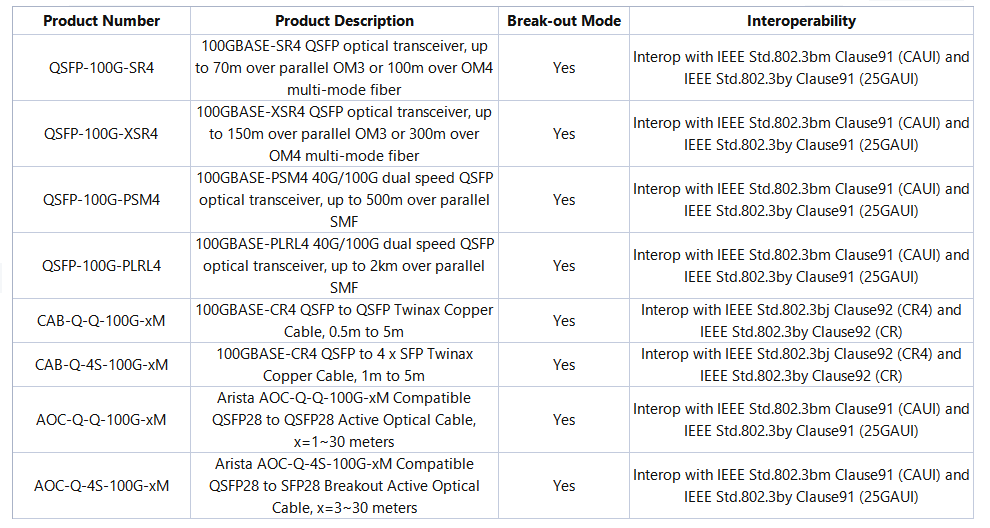
Several Arista 100G transceivers and cables can be used in breakout mode, which means they can be split into four 25G channels. These include:
- QSFP-100G-SR4: 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP optical transceiver, up to 70m over parallel OM3 or 100m over OM4 multi-mode fiber
- QSFP-100G-XSR4: 100GBASE-XSR4 QSFP optical transceiver, up to 150m over parallel OM3 or 300m over OM4 multi-mode fiber
- QSFP-100G-PSM4: 100GBASE-PSM4 40G/100G dual speed QSFP optical transceiver, up to 500m over parallel SMF
- QSFP-100G-PLRL4: 100GBASE-PLRL4 40G/100G dual speed QSFP optical transceiver, up to 2km over parallel SMF
- CAB-Q-Q-100G-xM: 100GBASE-CR4 QSFP to QSFP Twinax Copper Cable, 0.5m to 5m
- CAB-Q-4S-100G-xM: 100GBASE-CR4 QSFP to 4 x 25GbE SFP Twinax Copper Cable, 1m to 5m
- AOC-Q-Q-100G-xM: 100GbE QSFP to QSFP Active Optical Cable, 1m to 30m
- AOC-Q-4S-100G-xM: Arista AOC-Q-4S-100G-xM Compatible QSFP28 to 4x25G SFP28 Breakout Active Optical Cable, 3m to 30m
These transceivers and cables are interoperable with relevant industry standards when used in the breakout mode, as shown in the table below:
Arista Networks offers a variety of 100G transceivers designed to meet the high-performance networking needs of data centers, cloud computing environments, and enterprise networks. Here’s an overview of some of their key 100G transceiver options:
1. QSFP28 Transceivers
QSFP28 transceivers are the most common form factor for 100G Ethernet, providing high-density and low-power solutions.
Types of QSFP28 Transceivers:
100GBASE-SR4:
Description: Designed for short-range multimode fiber (MMF) applications.
Distance: Up to 70 meters on OM3 MMF, and up to 100 meters on OM4 MMF.
Wavelength: 850 nm.
Fiber/Cable: 12-fiber MPO connector.
100GBASE-LR4:
Description: Designed for long-range singlemode fiber (SMF) applications.
Distance: Up to 10 km.
Wavelength: 1310 nm (using WDM to multiplex four wavelengths).
Fiber/Cable: Duplex LC connector.
100GBASE-CWDM4:
Description: Uses coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) for intermediate range.
Distance: Up to 2 km on SMF.
Wavelength: 1271 nm, 1291 nm, 1311 nm, 1331 nm.
Fiber/Cable: Duplex LC connector.
100GBASE-PSM4:
Description: Uses parallel singlemode fiber for short to intermediate range.
Distance: Up to 500 meters on SMF.
Wavelength: 1310 nm.
Fiber/Cable: 12-fiber MPO connector.
100GBASE-ER4:
Description: Designed for extended range SMF applications.
Distance: Up to 40 km.
Wavelength: 1310 nm (using WDM to multiplex four wavelengths).
Fiber/Cable: Duplex LC connector.
100GBASE-SWDM4:
Description: Uses short wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM) for MMF applications.
Distance: Up to 100 meters on OM4 MMF.
Wavelength: 850 nm, 880 nm, 910 nm, 940 nm.
Fiber/Cable: Duplex LC connector.
2. 100G AOC and DAC Cables
Active Optical Cables (AOCs):
Description: Integrated solution with transceivers and fiber optic cable.
Distance: Typically up to 100 meters.
Use Case: High-density connections within racks or between adjacent racks.
Direct Attach Copper Cables (DACs):
Description: Integrated copper cable with QSFP28 connectors.
Distance: Typically up to 5 meters.
Use Case: Cost-effective solution for short-distance connections within racks.
3. 100G DWDM Transceivers
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing):
Description: Enables high-capacity data transmission over long distances by using multiple wavelengths on a single fiber.
Distance: Varies based on the deployment scenario and amplification.
Wavelength: Specific channels within the DWDM grid.
Use Case: Metro and long-haul networks requiring high bandwidth and extended reach.
Key Considerations for Choosing Arista 100G Transceivers
Application Needs:
Determine if your requirement is for short-range (SR), long-range (LR), or extended range (ER) applications.
Fiber Type:
Choose transceivers compatible with your existing fiber infrastructure (MMF or SMF).
Distance:
Match the transceiver specifications with the required transmission distance.
Form Factor Compatibility:
Ensure the transceivers are compatible with your networking equipment’s ports (e.g., QSFP28).
Cost:
Consider the cost of transceivers and the associated fiber optic cabling.
Future-Proofing:
Choose transceivers that support potential future network upgrades and expansions.
Conclusion
Arista’s 100G transceivers offer a range of options to suit different networking needs, from short-range data center connections to long-distance telecommunications. Selecting the right transceiver involves evaluating your network’s specific requirements in terms of distance, bandwidth, fiber type, and budget.