With the increasing development of optical fiber networks, optical fiber terminals using fusion splicing or mechanical fusion have become common. Because optical fibers are sensitive to pulling, bending, and crushing forces, use fiber splice trays to provide secure routing and an easy-to-manage environment for fragile fiber splices. In the past, fiber optic splice trays were usually installed in a box that hung on the wall. Today, fiber splice trays can be found in many places in fiber optic networks. This article will explain where fiber splice trays are needed and how to use them.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Fiber Splice Tray?
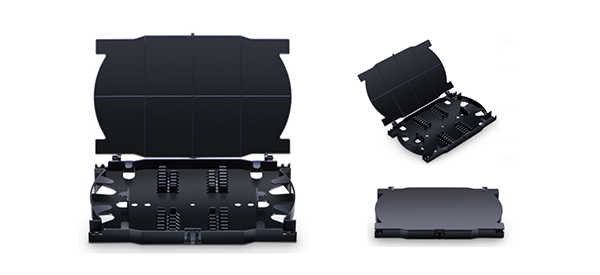
Fiber splice trays are typically used to hold and protect individual fiber splices. There are two main types of fiber optic connectors one is fusion splicing, and the other is mechanical splicing. Fiber splicing trays for fusion splicing and mechanical splicing are different. It is recommended to use dedicated fiber connector trays for different fiber connectors. Another important factor in a fiber optic splice tray is the number of fibers it can hold. Most fiber splice trays hold up to 24 fiber splices. The 12-core optical fiber splicing tray is the most used optical fiber splicing tray in the optical fiber network.
Where to Use Fiber Splice Tray
For most applications, fiber splice trays are not strong enough to provide strong protection for fiber splices alone, so they are often used with other components to protect the fiber: low space requirement and strong compatibility. Optical fiber splicing trays are usually used as accessories for other equipment, such as optical fiber splicing boxes, optical fiber distribution boxes, optical fiber housings, etc. The application of the fiber splicing tray is introduced in detail below.
Fiber Splice Tray in Fiber Optic Splice Closure
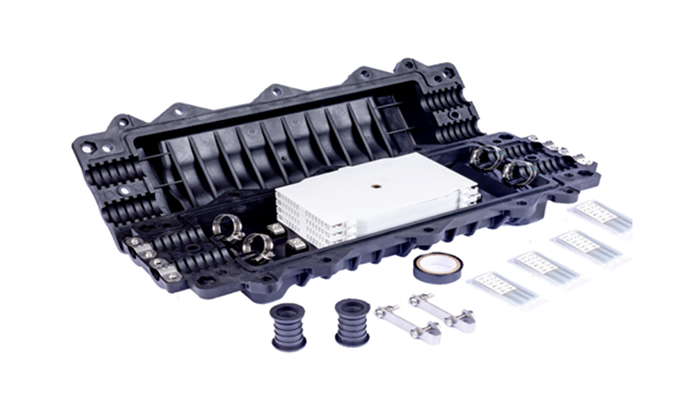
Fiber optic splice closures are widely used in today’s fiber optic networks for outdoor applications and harsh environments. It usually contains one or more fiber splice trays to provide space and protection for fiber splicing. Fiber splice trays used in different fiber splice closures may have different designs and fiber counts. Here we take the 96-fiber horizontal fiber optic splice closure and the 24-fiber dome fiber optic splice closure as examples.
The picture below shows the 96-core horizontal fiber splice box. It has two inputs and two outputs, providing space for 96 fiber optic connectors. Four standard 24-fiber fiber splice trays are stacked together in the fiber splice box.
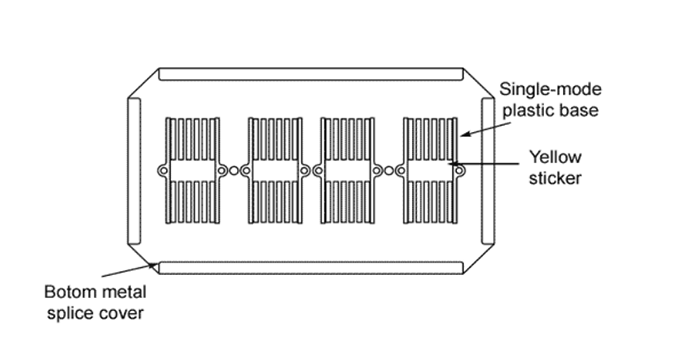
The 24-fiber splice closure has five entries providing up to 24 fiber optic splices in two 12-fiber splice trays. The two-fiber splice tray is designed to differ from the above ones, which is suitable for the vertical design of the fiber splice closure.
Fiber Splice Tray in Fiber Distribution Box
In FTTx projects, the service provider’s fiber optic cable usually must be connected to the fiber optic cable deployed near the end user. Fiber optic network installers typically splice feeder cables to end users through fiber splicing. Fiber distribution boxes are commonly used in FTTx projects to distribute a single fiber to individual end users. As shown in the figure below, fiber splicing trays are usually deployed in fiber optic distribution boxes to manage and protect fiber splicing.
Fiber Splice Tray in Fiber Enclosure
In addition to the above two applications, fiber optic splice trays are also popular in data centers and server rooms. Data centers typically avoid splicing fiber optic cables with fiber pigtails, which requires less space and provides better network performance than other fiber termination methods. Fiber splicing trays are typically installed in fiber optic housings to provide a safe and manageable environment for fiber splicing. Here we take the fiber splicing tray used in HOLIGHT’s FHD fiber optic cassette as an example, as shown in the figure below. It is a 96-fiber housing with four 24-fiber adapters on the front panel. The fiber optic housing holds four 24-fiber fiber splice trays, providing space for 96 fiber splices.
The Function of Fiber Splice Tray
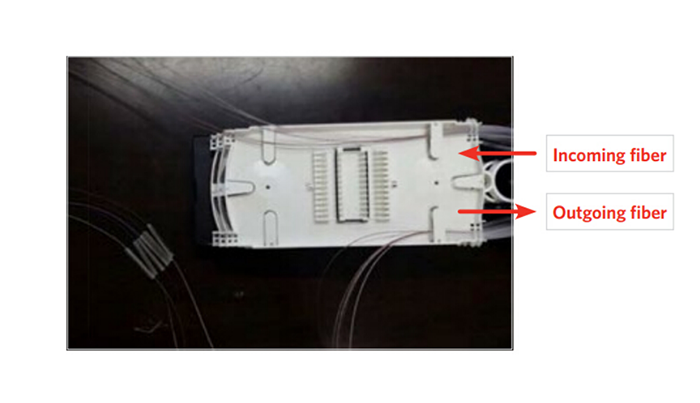
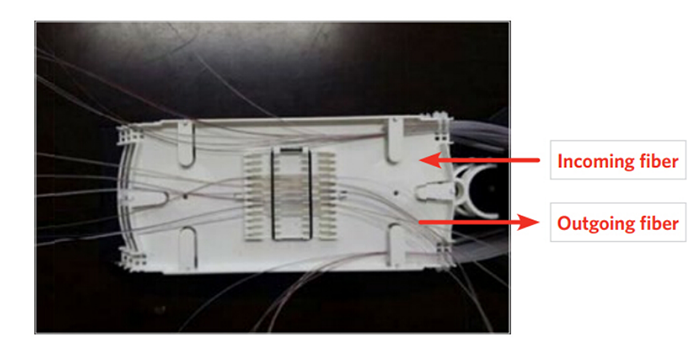
You might wonder how a fiber optic splice tray works with such a simple structure. The following briefly introduces its working function: The incoming cable is introduced into the welding center, and the cable’s outer sheath is stripped. The fiber then wraps completely around the tray and enters the splice frame. Different brackets are available for different types of connectors. Then, if the fiber is an intermediate point, it is fused to the drop cable; if it is a termination point, it is fused to the pigtail. They also wrap completely around the tray before being delivered from the tray.
Installation Procedures
The installation process can be broken down into five steps:
In step one, the fiber is routed into the splice tray using a screw conveyor or a fiber furcation tube and secured with cable ties.
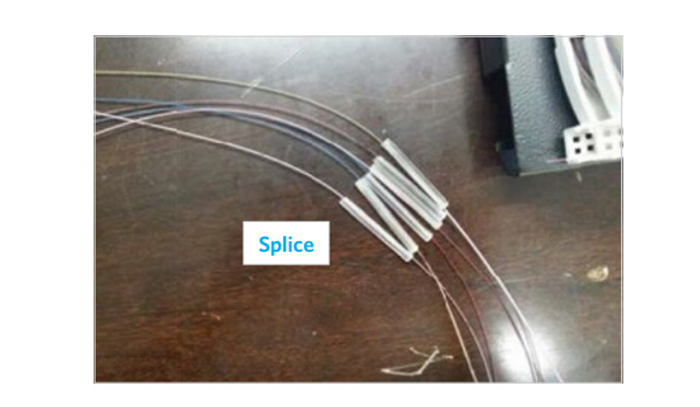
In step two, splice fibers per local practice.
In step three, place the spliced fibers into the color-coded ferrule holders
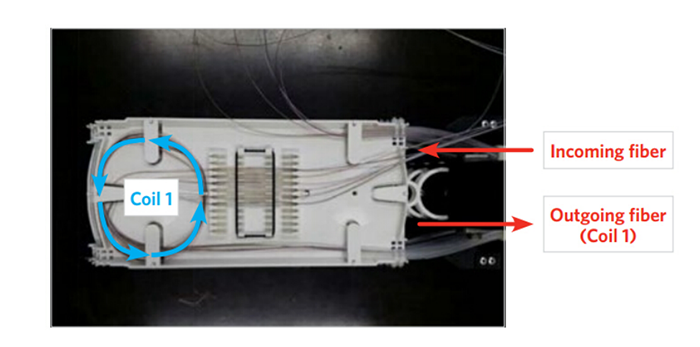
In step four, carefully wind the output fiber slack into the tray (coil 1).
In step five, carefully wind the incoming fiber slack into the tray (coil 2).
Applications
Optical fiber splice trays are usually placed in the middle of the route where cables need to be connected or at termination points and distribution frame points at the end of cable runs. Additionally, splices can be placed in splice trays, in splice boxes for OSP (Outdoor Plant) installations, or in patch panel boxes for indoor applications. Fiber optic splice trays are often integrated into patch panels to connect to fiber optics for indoor applications.