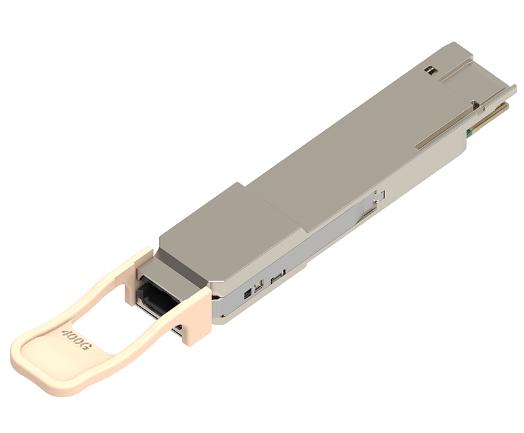
Mellanox MMA1B00-C100D Compatible 100G QSFP28 SR4 850nm 100m MTP/MPO MMF DDM Transceiver Module
Mellanox MMA1B00-C100D Compatible 100G QSFP28 SR4 Transceiver Module (850nm MMF 100m MTP/MPO DDM)The 100G QSFP28 SR4 transceiver modules are designed for 100G Ethernet links over multimode fiber. They are compliant with IEEE 802.3bm 100GBASE-SR4 and CAUI-4. Digital diagnostic functions are available through the QSFP28 MSA-specified I2C interface.
Table of Contents
ToggleProduct Details
| Mellanox Compatible | MMA1B00-C100D | Vendor Name | Walsun |
| Form Factor | QSFP28 | Max Data Rate | 103.1Gbps |
| Wavelength | 850nm | Max Distance | 100m on OM4 |
| Connector | MTP/MPO-12 | Transmitter Type | 850nm VCSEL |
| Cable Type | MMF | Receiver Type | PIN |
| TX Power | -8.4~+2.4dBm | Receiver Sensitivity | < -10.3dBm |
| Protocols | 100G Ethernet, MSA Compliant | Operation Temperature | 0 to 70°C (32 to 158°F) |
Applications:
Data Centers: QSFP28 transceivers are widely used in data centers to support high-speed interconnects between servers, storage systems, and network switches. Their high data rate and compact form factor make them ideal for the high-density environments typical of modern data centers.
Enterprise Networks: In enterprise networks, QSFP28 modules enable fast and reliable communication across different departments and locations. They support the seamless transfer of large files and the efficient operation of bandwidth-intensive applications.
Telecommunications: QSFP28 transceivers play a vital role in telecommunications infrastructure, facilitating high-speed data transmission over long distances. This supports the delivery of high-quality services to end-users, including internet, voice, and video.
What are the types and specifications of QSFP28 transceivers?
The types and main specifications of 100G QSFP28 are shown in the following diagram.
| QSFP28 | Industry Standards | Max Cable Distance | Optical Connector | Fiber Type to Be Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100GBASE-SR4 | IEEE 802.3bm, QSFP28 MSA, SFF-8665, SFF-8636, RoHS, CPRI, eCPRI | 100m | MTP/MPO-12 | MMF |
| 100GBASE-LR4 | IEEE 802.3ba 100GBASE-LR4, IEEE 802.3bm, QSFP28 MSA, SFF-8665, SFF-8636 | 10km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-ER4 | QSFP28 MSA Compliant | 40km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-ZR4 | QSFP28 MSA Compliant | 80km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-DR | IEEE 802.3cd 100GBASE-DR Specification compliant | 500m | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-FR | 100G Lambda MSA 100G-FR Specification compliant | 2km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-LR | 100G Lambda MSA 100G-LR Specification compliant | 10km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-PSM4 | QSFP28 MSA Compliant | 500m | MTP/MPO-12 | SMF |
| 100GBASE-CWDM4 | IEEE 802.3ba, IEEE 802.3bm, SFF-8665, SFF-8636, 100G CWDM4 MSA, QSFP28 MSA | 2km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-4WDM | QSFP28 MSA Compliant | 10km | LC Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-DWDM | IEEE 802.3bm, QSFP28 MSA, SFF-8636, SFF-8024 | 80km | CS Duplex | SMF |
| 100GBASE-BiDi | QSFP28 MSA Compliant | 20km | LC Simplex | SMF |
Future Prospects:
The demand for higher data rates and greater network efficiency continues to drive innovation in optical transceiver technology. The development of next-generation standards, such as 400G, and advancements in silicon photonics are set to further enhance the capabilities of optical modules like the QSFP28. These innovations promise to deliver even greater speeds, lower power consumption, and improved performance, ensuring that networks can keep pace with the ever-increasing demand for data.
FAQs on 100G QSFP28 Definition and Types
Q: What does QSFP28 stand for?
A: QSFP28 is abbreviated from Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable 28. The 100G QSFP28, implemented with four channels of high-speed differential signals with data rates ranging from 25Gbps up to potentially 40Gbps, is designed for 100 Gigabit Ethernet, EDR InfiniBand, and 32G Fibre Channel.
Q: What is the operating temperature range of 100G QSFP28 transceivers?
A: The standard operating temperature range of QSFP28 100G module commercial version is 0°C to 70°C and that of the industrial version is -40 to 85°C. Commercial version transceivers are generally applied. There are also some data centers that use 100G transceivers with operating temperatures ranging from 20°C to 50°C to reduce costs.
Q: Can I use QSFP+ optics on QSFP28 ports?
A: Yes, 100G QSFP28 ports can generally take either QSFP+ or QSFP28 optics. QSFP28 transceivers have the same form factor as the QSFP+ optical modules, and a QSFP28 module can break out into either 4x 25G or 4x 10G lanes, which depends on the transceiver used. It means that QSFP+ optics can be used on the QSFP28 ports at a lower 40G speed. However, QSFP28 modules can not be used on QSFP+ ports as the speed of the ports is lower than that of the optics used.
Q: Can 100G QSFP28 interfaces interoperate with SR10-based 100GbE?
A: No. The QSFP28 form factor has just 4 electrical lanes, which is not enough to support 10 lanes of 10G electrical interface. A QSFP 100G can only support a 4x 10G or 4x 25G electrical interface, which can be used as 4x 10GbE or 4x 25GbE, but not 10x 10GbE. As a result, the 100G QSFP28 interfaces cannot interoperate with SR10-based 100GbE transceivers.
Q: Can QSFP28 transceiver work with the CFP transceiver?
A: Yes, both are products of the Ethernet protocol and can interoperate with each other.
Q: How to achieve 100G to 4x 25G breakout application?
A: A simple 100G to 4x 25G breakout connection can be made between one QSFP28 SR4 transceiver and four SFP28 transceivers with breakout cables. In addition to 100G transceivers, breakouts can also be implemented with AOCs or DACs.
Q: Does the 100G QSFP28 need to use the FEC function?
A: Not all QSFP28 transceivers need FEC function, as the process of correcting error code will inevitably cause some data packet delay. FEC (Forward Error Correction) is a method to increase the credibility of data communication by correcting errors during signal transmission. When an error occurs in the transmission, the receiver is allowed to reconstruct the data. In the design of transceivers, the cost of FEC function is relatively high and is generally rarely used.
Q: What Parameters Will Influence 100G Transmission Performance?
A: In the process of the implementation of 100G Ethernet network, it may be influenced by several factors, such as the bandwidth, insertion loss, and so on.
- Skew: The first parameter that impacts 100G Ethernet transmission is skew. To be clear, skew means the time-of-flight difference between optical signals traveling on different fibers. As an inherent part of 100G Ethernet, skew is closely related to 100G Ethernet that uses parallel optics. In the parallel optic system, one data stream can be split into multiple data streams and transmitted over different fibers, allowing the use of lower-cost transceivers.
- Bandwidth: Bandwidth is another important factor that restraints 100G Ethernet. With enough bandwidth, the 100G Ethernet can achieve the transmission distance of at least 100m over OM3 and OM4 fibers, thus better meeting the requirements of businesses.
- Insertion loss: Most of the time, insertion loss refers to total optical power loss caused by an inserted component, such as a connector or coupler. It may be caused by air gaps between matching ferrules or loss of absorption due to scratches and contamination. The 100G Ethernet performance can be improved greatly with reduced insertion loss.
Related Article:
Huawei QSFP-100G-ER4-Lite Compatible 100G QSFP28 ER4 Lite 1310nm (LAN WDM) 40km with FEC, 30km without FEC LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
Mellanox MMA1L10-CR Compatible 100G QSFP28 LR4 1310nm (LAN WDM) 10km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
Juniper 100GBASE-ER4-D40 Compatible 100G QSFP28 Dual Rate ER4 1310nm (LAN WDM) 40km LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module
Huawei Compatible 100G QSFP28 BIDI TX1309nm-RX1304nm Single Lambda LC SMF 30km PAM4 DDM Optical Transceiver Module
HPE Aruba JL743A Compatible 100G QSFP28 ER4 Lite 1310nm (LAN WDM) 40km with FEC, 30km without FEC LC SMF DDM Transceiver Module