As the network becomes more complex with requests for higher bandwidth, data rates, and density, the market has seen a wide variety of transceiver modules in the telecommunication industry. SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, QSFP28, and OSFP are all form factor types of optical modules. The most typical function of these hot-swappable optical modules is to connect network switches and other network equipment (such as servers, etc.) for data transmission. QSFP and SFP are two Small Form-Factor Pluggable module types that have a significant influence on data communications. This post introduces QSFP vs SFP respectively and illustrates their difference in form factors, size, compatibility, and price.
Table of Contents
ToggleQSFP vs SFP – What is SFP?
First, let’s identify the relationships and differences between GBIC and SFP. SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) evolved from GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) but is designed with a smaller size. Since the SFP transceiver is more compact while maintaining the hot-swappable features of GBIC, SFP is also known as Mini GBIC. The size of an SFP with an LC head is only one-third to one-half the size of the GBIC module.
The SFP module is to bring higher port density for networking equipment, which caters to the trend of rapid development of the network. Hence, almost all mainstream system manufacturers have emitted the clumsy GBIC and replaced it with a smaller SFP. In the current market, the SFP optical transceivers occupy wide applications in telecommunications.

Figure 1: SFP transceiver module
QSFP vs SFP – What is QSFP?
The enhanced version of SFP is SFP+, which can only rate up to 10Gbps. However, the urgent need for higher-speed applications driven by growing business volume is always there. Here is where QSFP comes from.
QSFP, Quad SFP, or Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable interface, is derivated from the SFP. The word “Quad” points out there is a 4-channel interface while each channel carries up to 1Gbit/s to run at 4 Gbit/s totally.
How about QSFP+ and QSFP28? Both are the enhanced version of QSFP to meet the higher-speed requirement. QSFP has nearly been eliminated. QSFP vs QSFP+ and QSFP28 vs QSFP, what are the differences? In appearance, QSFP and QSFP+, and QSFP28 are exactly the same. The most notable difference lies in speed. To compare QSFP vs QSFP+, QSFP+ boosts the maximum data rates up to 40Gbps by 4-channel 10 Gbit/s or 1x 40G. To compare QSFP28 vs QSFP, QSFP28 speeds up each channel to 25Gbps to support a maximum data rate of 100Gbps by 4x 25G breakout connection, 2x 50G breakout, or 1x 100G.

Figure 2: QSFP+ transceiver module
QSFP vs SFP – What are the Differences Between SFP and QSFP?
Overview of the relationships between SFP and QSFP. In short, the SFP optics are developed from GBIC to offer a smaller size for high-density applications. QSFP modules are derivated from SFPs to provide fiber connectivity solutions with higher speed. The market utilizes 40G QSFP+ and 100G QSFP28 to meet higher-speed transmission requirements and gradually obliviates QSFP.
So what is it that highlights the difference between SFP and QSFP?
How to Choose SFP Transceivers?
In addition to SFP vs SFP+ vs QSFP, you’ll also need to consider the application. SFP transceivers are available in different types depending on what they will be used for, for example single-mode vs multimode SFP. Single-mode SFP transceivers work with single-mode fibre, whereas multimode SFPs are compatible with multimode fibre. Additionally, there are long-reach WDM SFP transceivers for multiplexing, simplex SFPs for single fibre applications, video SFP transceivers for transmission of high-definition video, and PON SFP transceivers for fibre-based access networks. SFPs are available in commercial and extended operating temperature ranges, with or without extended diagnostics capabilities.
QSFP vs SFP Form Factor
Compact, hot-swappable, and optical fiber connector are their common features. However, one can easily identify one from the other with a glance. QSFP vs SFP form factor is the key. Form Factor describes the attributes related to the design of SFP hardware, such as size and shape. The picture below shows the form factors of the different optical transceivers. You can figure out their appearance with ease.
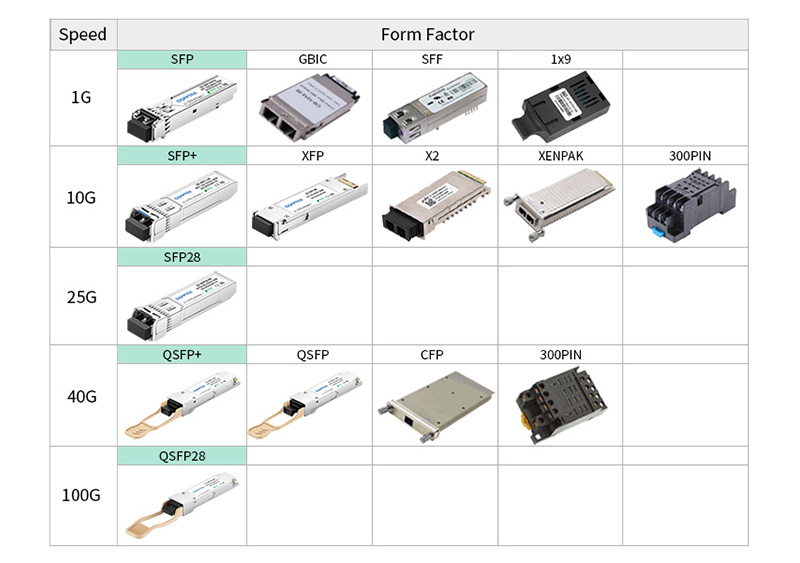
Figure 3: QSFP vs SFP vs other transceivers form-factors comparison
QSFP vs SFP Specifications
QSFP vs SFP specification is the second identification. Detailed factors include standard, connector, fiber type, wavelength, data rate, transmission distance, etc.
|
SFP |
QSFP+ |
QSFP28 |
|
|
Standard |
SFP MSA |
EEE 802.3ba QSFP+ MSA SFF-8436 SFF-8636 Infiniband 40G QDR |
IEEE 802.3bm QSFP28 MSA SFF-8665 SFF-8636 |
|
Fiber Type |
OM1 OM2 OS1 OS2 |
OM3 OM4 OS2 |
OM3 OM4 OS2 |
|
Wavelength |
850nm 1310nm 1550nm CWDM DWDM BIDI |
850nm 1310nm 832-918nm |
850nm 1310nm CWDM4 |
|
Data rate |
55Mbps 622Mbps 1.25Gbps 2.125Gbps 2.5Gbps 3Gbps 4.25Gbps |
40Gbps 41.2Gbps 42Gbps 44.4Gbps |
100Gbps 103Gbps 112Gbps |
|
Connector |
LC/SC/RJ45 |
LC/MTP/MPO |
LC/MTP/MPO-12 |
|
Max Distance |
160km |
40km |
80km |
|
DDM |
NO or YES |
YES |
YES |
|
Temperature |
COM/IND |
COM/IND |
COM/IND |
SFP is applied in SONET, Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and other communications standards. QSFP+, as the expansion of QSFP, supports 10-Gigabit Ethernet, 10G Fibre Channel, and InfiniBand.
In function capacity, QSFP vs SFP differs in the channel quantities and data rates.
SFP has only one channel while QSFP has four. SFP speeds up to 1Gbps, and SFP+ up to 10Gbps. However, The initial QSFP supports 4Gbps, and the new version QSFP+ supports 40Gbps. Further, a QSFP+ functions the same as 4 separate SFP+ modules, which means an increase in port density and overall system cost-efficiency.
Comparisons in SFP vs SFP+ vs SFP28 vs QSFP+ vs QSFP28
After figuring out what SFP/SFP+/SFP28/QSFP+/QSFP28 are, the following part will give detailed comparisons of SFP vs SFP+, SFP28 vs SFP+, QSFP vs QSFP28 and SFP28 vs QSFP28.
| Optic Types | Standard | Data Rate | Wavelength | Fiber Type | Max Distance | Typical Connector | DOM | OperatingTemperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFP | SFP | 155Mbps 1.25Gbps 2.5Gbps 3Gbps |
850nm 1310nm 1550nm CWDM DWDM BiDi |
MMF SMF |
160KM | LCRJ-45 | No or Yes | Commercial Industrial |
| SFP+ | SFP+ MSA |
6G 8G 10G |
850nm 1310nm 1550nm CWDM DWDM BiDi |
MMF SMF |
120KM | LCRJ-45 | Yes | Commercial Industrial |
| SFP28 | IEEE 802.3by SFP28 MSA SFF- 8472 SFF- 8432 |
25G 32G |
850nm 1310nm CWDM DWDM BiDi |
MMF SMF |
10KM | LC | Yes | Commercial Industrial |
| QSFP+ | IEEE 802.3ba QSFP+ MSA SFF- 8436 SFF- 8636 Infiniband 40G QDR |
40G 56G |
850nm 1310nm 832- 918nm |
MMF SMF |
40KM | LC MPO/MTP |
Yes | Commercial Industrial |
| QSFP28 | IEEE 802.3bm QSFP28 MSA SFF- 8665 SFF- 8636 |
100G | 850nm 1310nm |
MMF SMF |
80KM | LC MPO/MTP |
Yes | Commercial Industrial |
Conclusion
Transceiver modules are one of the most critical components in high-performance networking. Modern high-performance data network scenarios require the development of high-density, cost-effective, and low-power optical modules to improve performance. You will make the right decision as you understand the difference between SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, and QSFP28.
Are you still confused about the difference between SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+, and QSFP28? Still unsure which pluggable transceiver is best for your fiber optic cabling project? Or need help choosing between SFP and SFP+ QSFP? Contact Walsun of our transceiver experts, who can help you decide and put you on the right track.