Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Multimode Fiber?
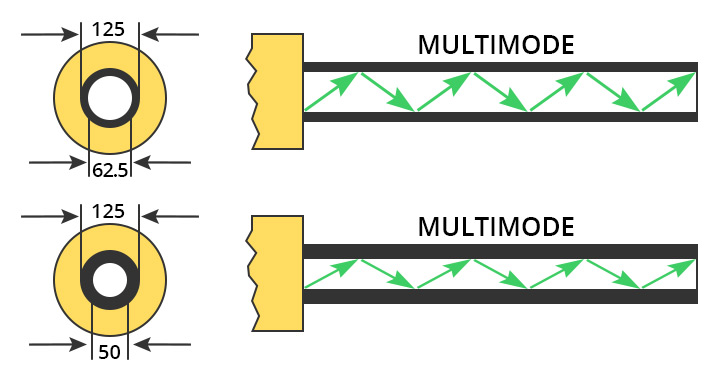
Multimode fiber (MMF) is a kind of optical fiber mostly used in communication over short distances, for example, inside a building or for the campus. Multimode fiber optic cable has a larger core, typically 50 or 62.5 microns that enables multiple light modes to be propagated. Because of this, more data can pass through the multimode fiber core at a given time. The maximum transmission distance for MMF cable is around 550m at the speed of 10Git/s. It can transmit farther at lower data rates, such as going about 2km at 100Mb/s.
OM1 and OM2
OM1 and OM2 are the two early forms of multimode cable that were offered. Both share an orange jacket color in accordance to industry standard. They both support a data rate of 1GB at 850nm. They’re also both used generally for short-distance transmissions such as short-haul networks, Local Area Networks (LANs) and private networks. OM1 has a core size of 62.5 um and is capable of distances up to 300 meters while OM2 has a core size of 50um and can travel up to 600 meters. Both OM1 and Om2 utilizes an LED light source for transmission, however OM1 is commonly used for 100Mbps applications which OM2 is generally used for 1000Mbps applications.
OM3 and OM4
OM3 and OM3 share many features including an aqua colored jacket, a core size of 50um, and a data rate of 10GB at 850nm. Unlike its predecessors both OM3 and OM4 utilizes lasers as a light source in order to support 10G, 40G, and 100G Ethernet. OM3 is capable of covering distances up to 300 meters. OM3 uses fewer modes of light thus enabling increased speeds, it is able to run 40GB or 100Gb up to 100 meters utilizing an MPO connector. OM3 is generally used in larger private networks. OM4 can cover distances up to 550 meters. OM4 can run 100Gb up to 150 meters using an MPO connector. It is commonly used in high-speed networks, data centers, financial centers, and corporate campuses.
OM5
OM5 is the newest type of multimode fiber cable and specifies a range of wavelengths between 850nm and 953nm. OM5 has a core size of 50um and comes in a lime green jacket. It was created in response to SWDM (short wavelength division multiplexing) technology which is now being used to transmit 40Gb and 100GB, SWDM allows OM5 to transmit multiple signals on a single fiber. By using a single fiber to transmit multiple signals OM5 is able to save fiber, especially when working with a 200G or 400G Ethernet network. OM5 is capable of carrying transmissions up to 150 meters.
OM1 vs OM2 vs OM3 vs OM4 vs OM5: What’s the Difference?
The prime distinction between multimode fibers rests on physical difference. Accordingly, physical difference leads to different transmission data rate and distance. Watch the following video to learn the differences between OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 & OM5 multimode fibers.
Physical Difference
Physical difference mainly lies in diameter, jacket color, optical source and bandwidth, which is described in the following table.
| MMF Cable Type | Diameter | Jacket Color | Optical Source | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM1 | 62.5/125µm | Orange | LED | 200MHz*km |
| OM2 | 50/125µm | Orange | LED | 500MHz*km |
| OM3 | 50/125µm | Aqua | VSCEL | 2000MHz*km |
| OM4 | 50/125µm | Aqua | VSCEL | 4700MHz*km |
| OM5 | 50/125µm | Lime Green | VSCEL | 28000MHz*km |
Practical Difference
Multimode fibers are able to transmit different distance ranges at various data rate. You can choose the most suited one according to your actual application. The max multimode fiber distance comparison at different data rate is specified below.
| MMF Category | Fast Ethernet | 1GbE | 10GbE | 40GbE | 100GbE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM1 | 2000m | 275m | 33m | / | / |
| OM2 | 2000m | 550m | 82m | / | / |
| OM3 | 2000m | / | 300m | 100m | 70m |
| OM4 | 2000m | / | 550m | 150m | 150m |
| OM5 | / | / | 550m | 150m | 150m |
What’s the Differences Between Single Mode and Multimode Fiber?
Technical difference
Core Diameter—Single mode fiber has a small diametral core(8.3 to 10 microns) that allows only one mode of light to propagate. Multimode fiber optic cable has a large diametral core(50 to 100 microns) that allows multiple modes of light to propagate.
Light Source—Multimode devices usually use a LED or laser as a light source. While single mode devices use a laser, or laser diode, to produce light injected into the cable.
Practical Difference
Distance—Light travels a longer distance inside single mode cable than it does inside multimode. So multimode fiber is suitable for short haul application, allowing transmission distances of up to about 550m at 10Git/s. When distance is beyond 550m, single mode fiber is preferred.
Price—Multimode fiber usually cost less than single mode fiber.
Bandwidth—The bandwidth of single-mode is higher than multimode as much as 100,000 GHz.
Conclusion
Due to its high capacity and reliability, multimode fiber is usually used for backbone applications in buildings, and it continues to be the most cost-effective choice for enterprise and data center applications up to the 500-600 meter range. But that doesn’t mean we can replace single mode fiber with multimode fiber cable. When deciding between a single mode fiber and a multimode fiber, it all comes down to the applications you need, the transmission distance you need to cover, and the overall budget you have.
You May Also be Interested