QSFP-DD-800G-2FR2 800G QSFP-DD800 2FR2 (200G per line) 2km 1291/1311nm Dual CS SMF Transceivers
Product Details
| Product Number | QSFP-DD-800G-2FR2 | Vendor Name | Walsun |
| Form Factor | QSFP-DD | Max Data Rate | 4x200G, 2x400GbE |
| Wavelength | 1291nm, 1311nm | Max Distance | 2km |
| Modulation Format | PAM4 | Host Required | FEC |
| Connector | Dual CS | Voltage Supply | 3.3V |
| Cable Type | SMF | DDM Support | Yes |
| Transmitter Type | EML | Receiver Type | PIN |
| TX Power | -3.2~+4.4dBm | Receiver Sensitivity | < -4.6dBm |
| Operation Temperature | 0 to 70℃ (32 to 158°F) | Maximum Power | < 16W |
| Protocols | IEE802.3ck, IEEE 802.3cu, QSFP-DD MSA | Application | 800G Ethernet, Data Center Interconnect, Infiniband Interconnects |
FAQS
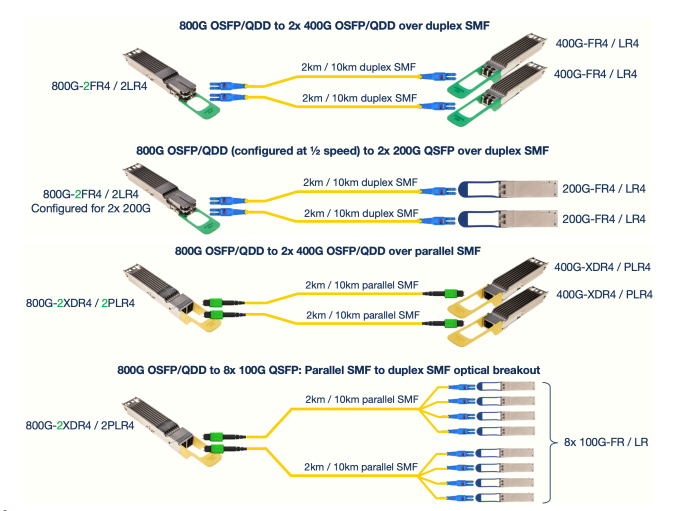
Q:Which 800G Transceivers and Cables can be used for optical or electrical breakout?
A:800G QSFP optics that support breakouts are summarized below. Arista 800G copper cables that support breakouts are described on the following page. In the tables below, the term “near end” transceiver refers to the transceiver / cable plugged into the 800G OSFP or QSFP-DD port, and the “remote end” refers to the “broken out” transceiver / cable connected to a 400G OSFP/QSFP-DD, 200G QSFP or a 100G QSFP.
| 800G Optical Module | Near end port config | Fiber type | Reach | Remote end |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSFP-800G-2FR4, or QDD-800G-2FR4 | 2x 400G-4 | 2 pairs of duplex SMF | 2km | 2x OSFP-400G-FR4 or 2x QDD-400G-FR4 |
| 2x 200G-4 | 2x QSFP-200G-FR4 | |||
| OSFP-800G-2LR4, or QDD-800G-2LR4 | 2x 400G-4 | 10km | 2x OSFP-400G-LR4 or 2x QDD-400G-LR4 | |
| 2x 200G-4 | 2x 200G-LR4 QSFP modules | |||
| OSFP-800G-2XDR4, or QDD-800G-2XDR4 | 2x 400G-4 | Parallel SMF (2x MPO-12) | 2km | 2x OSFP-400G-XDR4 or 2x QDD-400G-XDR4 |
| 8x 100G-1 | 8x QSFP-100G-FR | |||
| OSFP-800G-2PLR4, or QDD-800G-2PLR4 | 2x 400G-4 | 10km | 2x OSFP-400G-PLR4 or 2x QDD-400G-PLR4 | |
| 8x 100G-1 | 8x QSFP-100G-LR |
Q:What form-factors are used for 800G transceivers?
A:800G transceivers utilize the same form factors as 400G optics, namely the OSFP and QSFP-DD. FS offers support for both form factors, providing 800G platforms in OSFP and QSFP-DD variants.
-
- OSFP: The OSFP, which stands for “Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable,” is named “Octal” because its electrical interface consists of 8 electrical lanes. In the case of 800G, each electrical lane is modulated at 100Gb/s, resulting in a total bandwidth of 800Gb/s.
- QSFP-DD: The QSFP-DD, which stands for “Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable – Double Density,” shares a similar form factor with the QSFP but features an additional row of electrical contacts to accommodate more high-speed electrical lanes. While a QSFP has 4 high-speed electrical lanes, a QSFP-DD has 8. In the context of 800G, each electrical lane of the QSFP-DD operates at 100Gb/s, providing a total bandwidth of 800Gb/s.
Q:Can OSFPs be plugged into a QSFP-DD port, or QSFP-DD’s plugged into an OSFP port?
A:No. The OSFP and the QSFP-DD are two physically distinct form factors. For OSFP systems, OSFP optics and cables must be used, and for QSFP-DD systems, QSFP-DD optics and cables must be used.
Q:How many electrical lanes are used by the 800G transceivers?
A:The 800G transceivers utilize 8x electrical lanes in each direction, with 8 transmit lanes and 8 receive lanes.
Q:What are the speed and modulation formats used by 800G OSFP/QSFP-DD modules?
A:As said before, all 800G modules make use of 8x electrical lanes in both directions, comprising 8 transmit lanes and 8 receive lanes. Each lane operates at a data rate of 100G PAM4, resulting in a total module bandwidth of 800Gb/s. Additionally, the optical output of all 800G transceivers comprises 8 optical waves, with each wave modulated at 100G PAM4 per lane.
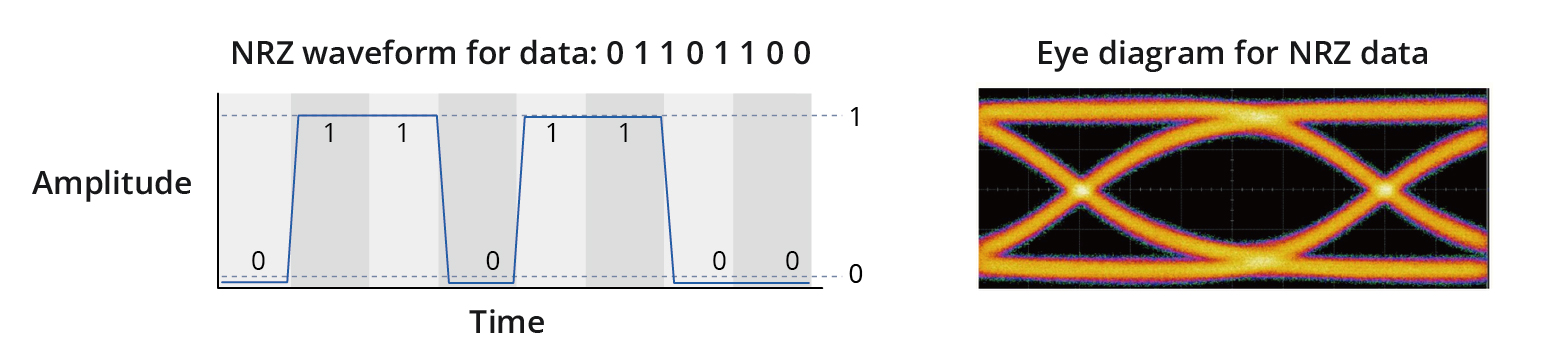
Q:What is the significance of PAM4 or NRZ modulation for electrical or optical channels?
A:NRZ, which stands for “Non Return to Zero,” refers to a modulation scheme used in electrical or optical data channels. It involves two permissible amplitude levels or symbols, with one level representing a digital ‘1’ and the other representing a digital ‘0’. NRZ is commonly employed for data transmission up to 25Gb/s and is the simplest method for transmitting digital data. An example of an NRZ waveform, along with an eye diagram illustrating NRZ data, is depicted below. An eye diagram provides a visual representation of a modulation scheme, with each symbol overlapping one another.
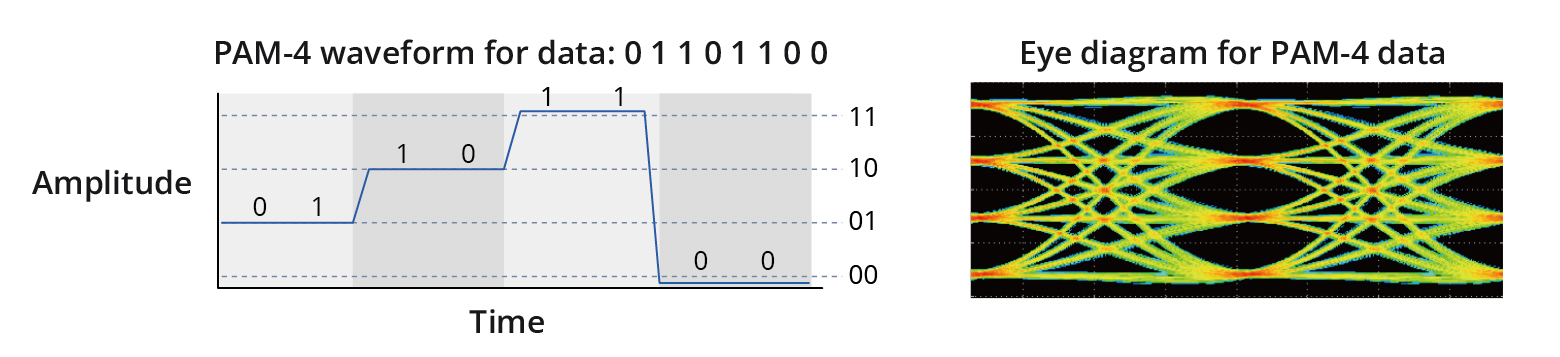
PAM4, on the other hand, stands for Pulse Amplitude Modulation – 4, with the ‘4’ signifying the number of distinct amplitude levels or symbols in the electrical or optical signal carrying digital data. In this case, each amplitude level or symbol represents two bits of digital data. Consequently, a PAM4 waveform can transmit twice as many bits as an NRZ waveform at the same symbol or “Baud” rate. The diagram below showcases a PAM4 waveform along with an eye diagram for PAM4 data.
Q:What is the maximum power consumption of 800G OSFP and QSFP-DD transceivers?
A:The power consumption of 800G transceivers varies between 13W and 18W per port. To obtain specific power consumption values for individual modules, please consult each transceiver’s datasheet.
Q:Do Walsun 800G transceivers support backward compatibility?
A:The backward compatibility of 800G transceivers depends on the specific design and implementation. Some 800G transceivers are designed to be backward compatible with 400G or 200G transceivers, allowing for a smooth transition and interoperability within existing networks. For example, Walsun 800G OSFP SR8 transceiver supports 800G ethernet and breakout 2x 400G SR4 applications. However, it is important to check with the module manufacturer for specific compatibility details.
Q:What standards govern 800G transceivers?
A:Standards for 800G transceivers, such as form factor specifications, electrical interfaces, and signaling protocols, are typically governed by industry consortiums like the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), the OIF (Optical Internetworking Forum), and the QSFP-DD MSA (Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable – Double Density Multi-Source Agreement).
Q:What are the key features of the Walsun 800G transceivers?
A:Key features of? Walsun 800G optical module typically include support for multiple modulation formats, high data transfer rates, low power consumption, advanced error correction mechanisms, compact form factors (e.g., QSFP-DD800 or OSFP), and interoperability with existing network infrastructure.